Pay attention to a balanced diet
Reduce salt intake: Have you ever wondered why you have particularly swollen legs after a salt-rich dinner like pizza or fast food? Salt can exacerbate fluid retention. Try to enrich your diet with less salty foods. Instead of reaching for chips and salty snacks, opt for fresh, unprocessed foods to reduce swelling.
Eat potassium-rich foods: Perhaps you've noticed that your swelling doesn't go down despite a healthy diet. Potassium-rich foods like bananas and spinach can help your body expel excess water and thus reduce swelling. These small changes in your diet can make a big difference.
Drink enough water: Do you find it difficult to drink enough water, especially when you're busy? It may seem counterintuitive, but adequate hydration can actually help reduce water retention. Set small goals, such as always having a water bottle within reach, to remind yourself of your daily water intake.
Regular exercise
Engage in regular exercise: The thought of additional physical activity can be overwhelming, especially if you already have a full schedule. However, regular exercise is crucial for blood circulation. Even a short walk in the evening or a few minutes of light gymnastics can help you drain fluids from your legs and improve symptoms.
Elevate legs: If you sit at a desk all day, you might be familiar with the feeling of heavy, swollen legs. A simple trick to counteract this is to elevate your legs during your breaks. Raise your legs for 15 to 20 minutes to reduce swelling and promote blood flow.
Use compression stockings
Use compression stockings: You might know this: Your legs feel heavy and tired after a long day. Compression stockings can help you. They apply pressure, thereby supporting the function of the venous valves and helping to reduce swelling. They can be very helpful, especially on long trips or stressful days.
Choose the right size: Make sure that the compression stockings fit well and are not too tight. It is important that they fit optimally to achieve the best possible effect. Therefore, take exact measurements and refer to the manufacturer's specifications for size selection. Your doctor or pharmacist can also help you choose the right size and compression strength.
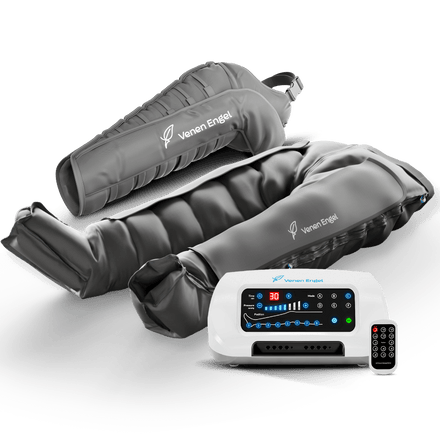
Compression massage
Use compression massage devices: After a strenuous day, it is often difficult to find time for additional treatments. If you want to relax at home, schedule regular sessions with your Venen Engel. It applies gentle pressure to your legs and supports lymphatic flow, which can help you feel better faster. It can help alleviate your symptoms and give you a sense of relief and comfort.
Medical support
Have your symptoms checked: If you regularly struggle with water retention and the usual tips don't help, it's important to consult your doctor. He or she can help you identify the exact cause and find appropriate treatment options.
Discuss alternatives: If you are taking medications or hormonal contraceptives that may contribute to water retention, talk to your doctor about possible alternatives. Sometimes a change in medication or another therapy option can be helpful.